If you are responsible for a business’ or organization’s budgeting and accounts payable, you know that there is a massive cost associated with printing. Not only are there the paper costs, but there are costs for ink, toner, and the sometimes-all-too-frequent printer repair. However, it is important not to overlook that there is also an environmental cost associated with this printing. Paper production destroys trees, and the disposal of paper products results in unwanted CO2 emissions. Some have looked towards digital signage as a way of reducing their printing requirements and reducing the environmental impact of their business. In this article, we examine how useful digital signage can be in achieving that goal.
Does digital signage or printing have a larger carbon footprint?
To carry out such an analysis, we must first make an estimate regarding the average printing activity per employee. According to printing company Ray Morgan, the “typical office worker prints 10,000 pages per year.”
Next, we must make an assumption regarding how much of this printing can be replaced by digital signage. Of course, certain printing activities, such as printing contract documents that require signatures, cannot be replaced by digital signage. However, other printing activities, such as printing promotional material and office communication documents, can be replaced by digital signage. Let’s make a conservative estimate that digital signage can replace just 10% of office printing. This translates to 1,000 pages per employee per year.
To assess the environmental impact of all this printing, we need to apply an estimate regarding the total CO2 emissions from this printing. According to Standard Carbon, 500 sheets of paper produces approximately 4.59 lbs of CO2 emissions. If an employee would otherwise print an additional 1,000 pages per year if their organization did not have digital signage, this would translate to 9.18 lbs of (potentially avoidable) CO2 emissions per year. So, can an organization produce less CO2 emissions if they replace these 1,000 pages per employee per year with a digital signage solution? Let’s find out.
To run a digital signage display, an employee must power a digital signage player and an actual display screen. Screenly’s Raspberry Pi based digital signage player requires approximately 3 watts to run. According to ElectricityPlans, a standard 50 inch LED screen requires approximately 16 watts to run. To run together, these devices require a combined 0.019 kilowatts. If these devices are running 24/7, that is for all 8760 hours per year, the devices require a total of 166.44 kilowatt-hours of energy per year.
The next step is to determine the CO2 emissions from 166.44 kilowatt-hours of energy per year. Of course, this is in part a function of the way in which the energy was originally produced. Electricity generated from burning fossil fuels has a much higher CO2 emission per kilowatt-hour than electricity generated via solar cells! To consider these differences in electricity production, we can simply use an average estimate for the CO2 emissions generated per kilowatt-hour of electricity produced (in this average, we seek to consider the share of multiple energy production methods that power the current electricity grid). According to Carbonfund.org, a reasonable average estimate of CO2 emissions per kilowatt-hour given current, average energy production methods is 1.222 lbs of CO2 emissions per kilowatt-hour. So, our 166.44 kilowatt-hours of energy per year that are consumed by a single digital signage display and a Screenly digital signage player combined result in approximately 203.39 lbs of CO2 emissions per year.
Let’s now do some final calculations. Our last step is to make an estimate on how many employees can be served from a single digital signage display and digital signage player - you do not need one setup per employee, of course. Let’s again make a conservative estimate and assume that a single digital signage display and digital signage player can serve the needs of 50 employees. Our 203.39 lbs of CO2 per year from digital signage then translates to 4.07 lbs of CO2 emissions per year per employee.
As stated in the previous paragraphs, businesses would have 9.18 lbs of CO2 emissions per year per employee if digital signage communications were instead passed on via print. In conclusion, according to our estimates, digital signage can cut a company’s CO2 emissions by over 55%. This is a massive impact, and, if any business is able to achieve a reduction in their CO2 emissions by over 55%, such an event should be greatly celebrated.
Applying the same analysis for other digital signage players
It is important to highlight here that the Raspberry Pi is an incredibly energy efficient digital signage player. Requiring just 3 watts to run, the Raspberry Pi has a much lower energy requirement than its rivals. This is why Screenly digital signage players are based off of Raspberry Pi hardware.
In order to demonstrate the impressive energy efficiency of Raspberry Pi based digital signage players, we list a few other digital signage players, their corresponding energy usage, and their estimated carbon footprint per year per employee. To arrive at these estimated carbon footprint, we simply plug in the energy requirements for each digital signage player into the analysis performed in the previous section. In the table below, we list five digital signage players, and in the rows we list the watts each one takes to run, the CO2 emissions per employee per year when these players are used with the aforementioned 50” display, and the percent change in CO2 emissions when compared to CO2 emissions that would otherwise come from printing.
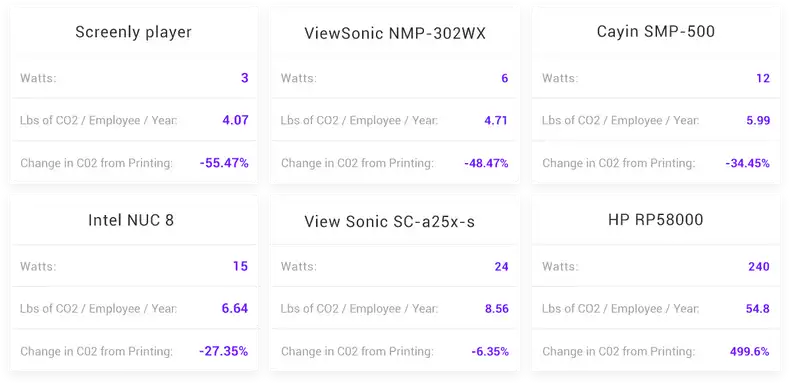
As seen above, the energy consumption of your digital signage player really matters in determining if your digital signage efforts will help your business “go green.” The ViewSonic NMP-302WX and Cayin SMP-500 digital signage players yield an admirable 48.47% and 34.45% decrease in CO2 emissions when compared to CO2 emissions from printing. The popular Intel NUC 8 digital signage player, a Windows 10 supporting mini-computer, yields a 27.35% decrease in CO2 emissions. However, a Raspberry Pi based digital signage player outcompetes all three of the previous players with a 55.47% decrease in CO2 emissions. It is a great accomplishment of the Screenly development team to have pushed the limits of such a simple, low-powered device such that it can support the robust and reliable digital signage solution that is Screenly. The ViewSonic SC-A25X-S digital signage player only yields a relatively minimal 6.35% decrease in CO2 emissions, and, importantly the HP RP5800 digital signage player actually yields an increase in CO2 emissions of 499.6%. Accordingly, you must really dig into the details of the power requirements for your chosen digital signage hardware. If you are not careful, some digital signage solutions can actually result in an increase in your organization’s CO2 emissions.
Interested in learning more?
If you found this analysis helpful, stay tuned, as we will continue to post similar articles with numbers and calculations that are catered to specific digital signage use cases and industries. Additionally, while this article covers the relative CO2 emissions and environmental costs for digital signage versus printing, be sure to also check out our article that compares the financial costs of different digital signage players.